AiTM PHISHING ATTACKS
Many large organisations are falling prey to different types of attacks every day. Microsoft recently released a detailed view of an AiTM (Adversary -In-The-Middle) phishing attack that targeted thousands of users using Microsoft authentication landing pages.
Security professionals and researcher alike agree that passwords are less secure and not recommended as a standalone security feature. Many organisations are steadily advocating the use of MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) as an additional security measure, moreover, stressing on an MFA solution that is Phishing-Resistant. The recent revelation by Microsoft on AiTM phishing using their landing pages is a major concern since it by passes the traditional MFA solutions.
It is important to note that these attacks are not limited to Microsoft only, many organisations use other products such as Google or many other cloud identity services as their identity providers. Phishing campaign tools used by attackers make their lives easier by cloning websites even with the organisation’s branding to deceive victims.
HOW DOES AiTM ATTACK HAPPEN?
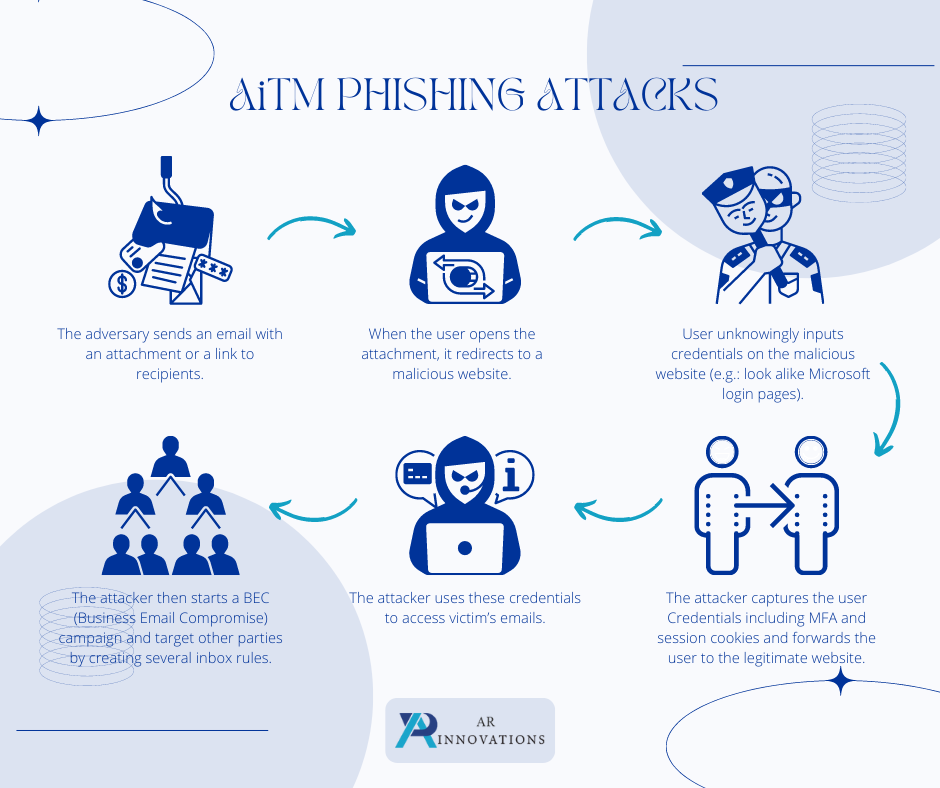
- The adversary sends an email with an attachment or a link to recipients.
- When the user opens the attachment, it redirects to a malicious website.
- User unknowingly inputs credentials on the malicious website (e.g., look alike Microsoft login pages)
- The attacker captures the user Credentials including MFA and session cookies and forwards it to the legitimate website.
- The attacker uses these credentials to access victim’s emails
- The attacker then starts a BEC (Business Email Compromise) campaign and target other parties by creating several inbox rules.
HOW DO WE DEFEND AGAINST SUCH ATTACKS?
There are three controls through which an organisation can safeguard themselves from such attacks:
- A well-established security awareness training and testing program
- Two Factor Authentication based on the following technologies
- Phishing-Resistant MFA solutions such as FIDO v2.0 (e.g., Windows Hello. FIDO Keys)
- Certification-based authentication (Digital Certificates).
- A process to verify with the supplier when a change in account number is requested by them to defend against Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks.
WHAT IS FIDO?
FIDO (Fast Identity Online) is a protocol used for authentication which works based on public key Infrastructure (PKI). FIDO can be used in 2 mains ways, platform-based (Windows Hello) or a FIDO Key with a fingerprint or PIN, which a user can plug in to the device for authentication. The important aspect of FIDO is that a user will locally authenticate a FIDO device or FIDO certified system first and then authentication happens with the online service.
FIDO basically protects the secret that proves who you really are locally, and not in an external server. Which makes it highly secure and private since only the user can authenticate the FIDO device or system.
Organisations can use FIDO certified devices and products such as FIDO Keys to protect the organisation and provide a Phishing-Resistant MFA solution.
WHAT IS CERTIFCATION-BASED AUTHNTICATION?
On the other hand, organisation can also make use of certification-based authentication, digital certificates also make use of the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). As an organisation you can obtain a certificate from a reputed authority called a Certificate Authority (CA) e.g., DigiCert, GoDaddy and use that as a password-less authentication method. Unlike FIDO the administrators of the systems are responsible for the digital certificates.
It is imperative that organisations make use of FIDO and certificate-based authentication as their MFA solution as opposed to traditional, less secure MFA solutions such as SMS OTP, Email OTP or Authenticator apps which are increasingly proving to be vulnerable to modern attacks. Organisations who have a critical threat landscape must do a risk assessment and adapt to these newer technologies to protect their assets, since all it takes is one individual clicking on a link or downloading an attachment.




